"Exploring the Power of Linux Shell Scripting: Innovative Project Ideas and Implementation"
"Enhance Efficiency, Automation, and System Management with Linux Shell Scripting"
Introduction:
Welcome to the world of Linux shell scripting, where command-line mastery meets automation and efficiency. In this blog post, we'll dive into five innovative projects that harness the potential of shell scripting to streamline tasks and boost productivity. From smart backups to interactive task management, these projects will empower you to leverage the full capabilities of the Linux command line. Get ready to unlock the true power of shell scripting and take your command line skills to new heights.
Let's get started!
Smart Backup System: "Automate Your Backups with a Smart Backup System Using Linux Shell Scripting":-
Process for the Smart Backup System Script:
Set the source and destination directories: Modify the
source_dirandbackup_dirvariables in the script specify the source directory containing the files you want to back up and the destination directory where the backups will be stored.Check if the backup directory exists: The script checks if the backup directory specified
backup_direxists. If it doesn't, the script creates it using themkdir -pcommand.Iterate over files in the source directory: The script uses a
forloop to iterate over each file in the source directory ($source_dir/*).Check file modification status: For each file, the script checks if it has been modified since the last backup. It compares the modification time of the file (
$file) with the corresponding file in the backup directory ($backup_dir/$(basename "$file")) using the-ntoperator.Backup the file: If the file has been modified, the script copies it to the backup directory using the
cpcommand. The destination path for the backup is constructed by appending the base name of the file ($(basename "$file")) to the backup directory path.Display backup status: After backing up a file, the script outputs a message using the
echocommand to indicate that the file has been successfully backed up.
You have to customize this script by replacing /path/to/source it with the actual path of your source directory and /path/to/backup with the desired path for the backup directory. Additionally, you can modify the backup logic to suit your specific requirements, such as excluding certain file types or implementing versioning.
Example Of Shell Script:-
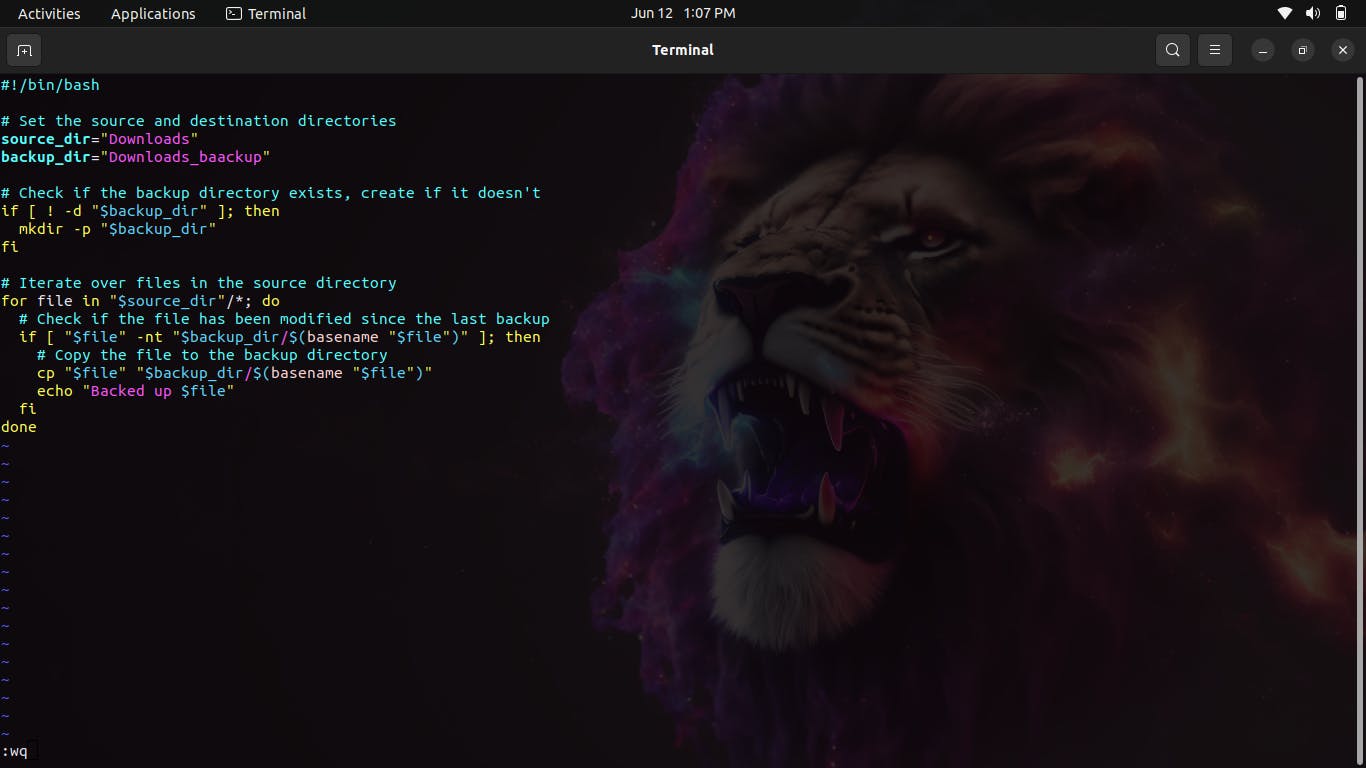
#!/bin/bash
# Set the source and destination directories
source_dir="/path/to/source"
backup_dir="/path/to/backup"
# Check if the backup directory exists, create if it doesn't
if [ ! -d "$backup_dir" ]; then
mkdir -p "$backup_dir"
fi
# Iterate over files in the source directory
for file in "$source_dir"/*; do
# Check if the file has been modified since the last backup
if [ "$file" -nt "$backup_dir/$(basename "$file")" ]; then
# Copy the file to the backup directory
cp "$file" "$backup_dir/$(basename "$file")"
echo "Backed up $file"
fi
done
To execute the Smart Backup System script using a Linux terminal, follow these steps:
Open a Linux terminal by launching the terminal application on your system. You can usually find it in the applications menu or by using a keyboard shortcut (e.g., Ctrl+Alt+T).
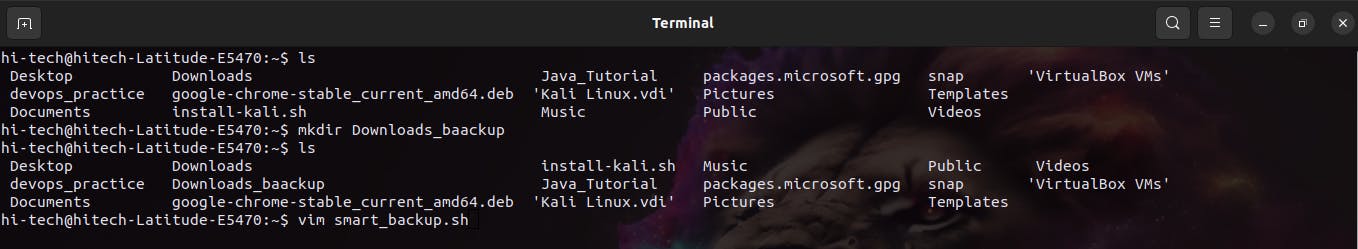
Make a file in the particular directory where you wanna Execute the script for example by commanding
vim smart_backup.shStart Writing the shell script in the vim file by pressing the
'I'button and after writing it press theEscbutton and then to save it pressshift+:and thenwq+Enter.Make the script executable by running the command
chmod +x script_name.sh, replacingscript_name.shwith the actual name of the script file. This command grants execute permissions to the script.Execute the script by typing
./script_name.shand pressing Enter. Again, replacescript_name.shit with the actual name of the script file. The./prefix is necessary to indicate that the script is located in the current directory.The script will start running and perform the backup process based on the specified source and destination directories. It will check if the backup directory exists and create it if necessary. Then, it will iterate over the files in the source directory, comparing the modification time of each file with its counterpart in the backup directory. If a file has been modified, it will be copied to the backup directory with the same filename. The script will display a message for each file that is successfully backed up.
Monitor the terminal for any output or messages generated by the script. Once the script finishes executing, you can check the backup directory to verify that the files have been backed up successfully.
That's it! You have successfully executed the Smart Backup System script using the Linux terminal. Feel free to adjust the source and destination directories in the script according to your specific requirement.
Real-Time Execution Example:-
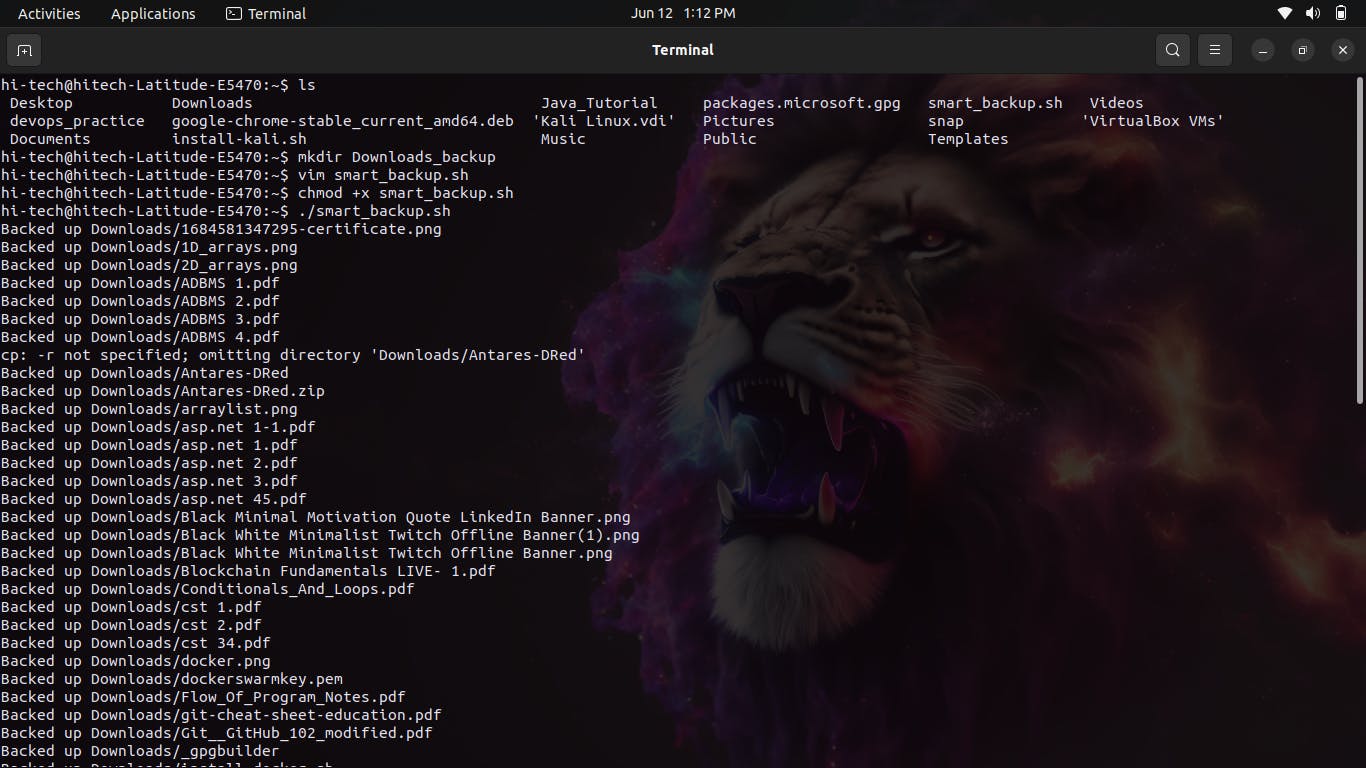
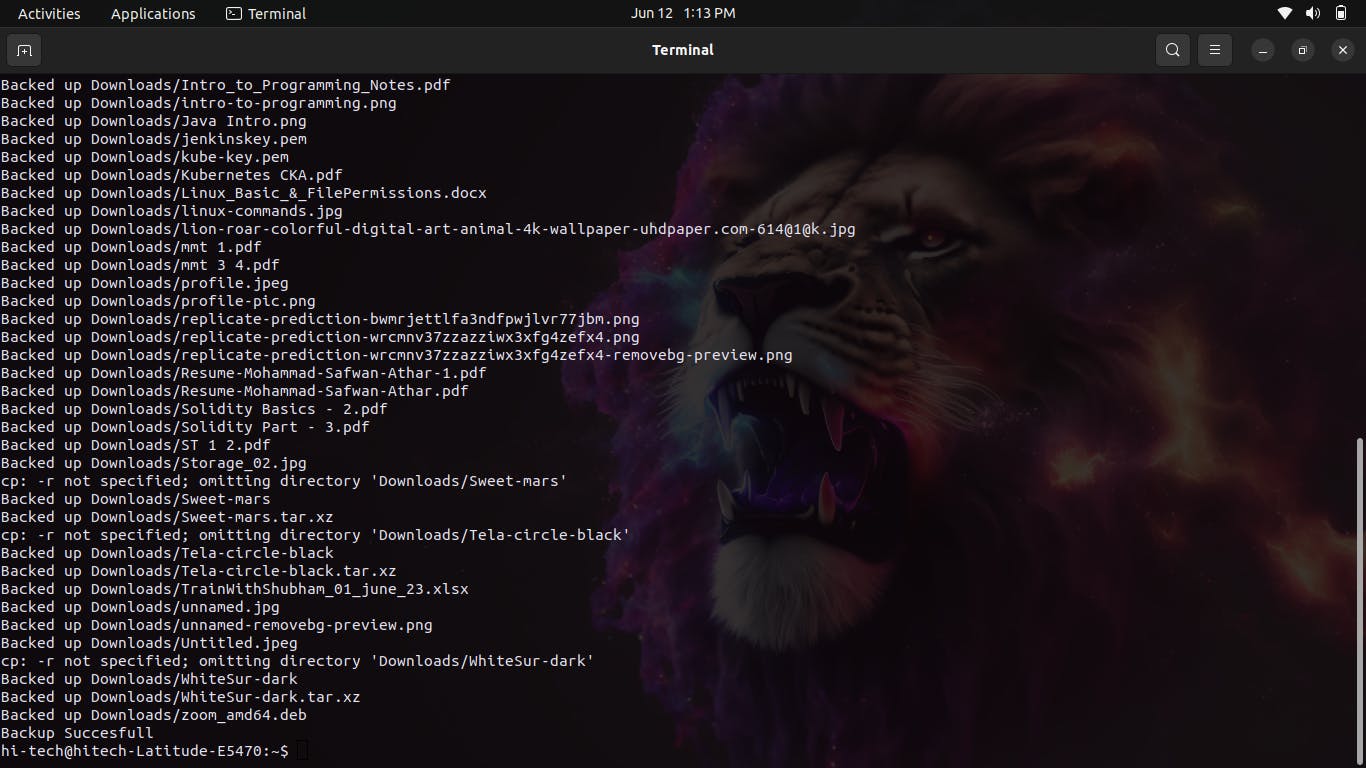
Hence Backup was Successfully Completed!
#DevOps #Linux #Shellscripting #project #msatechnohub